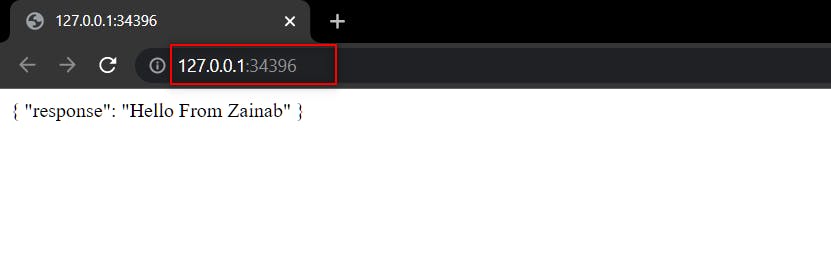
Create a NodeJS application
npm init
npm install express
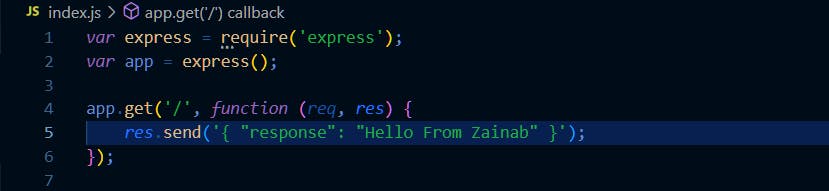
Create index.js and paste the following code
Create Docker file
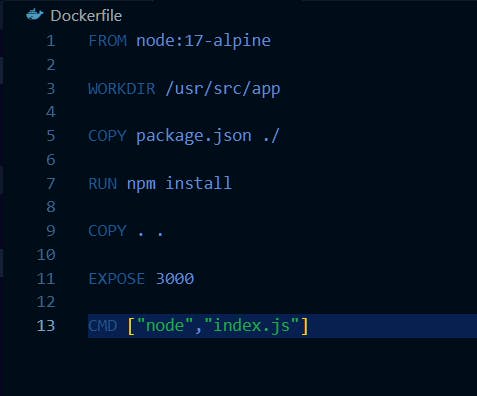
FROM node:17-alpineThis line specifies the base image to use for the container.WORKDIR /usr/src/appThis line sets the working directory for the container to/usr/src/appThis is where the application code and its dependencies will be copied to.COPY package.json ./This line copies thepackage.jsonfile from the host machine to the/usr/src/appdirectory in the container. This file contains information about the application's dependencies, which will be installed in the next step.RUN npm installThis line runs the commandnpm installinside the container to install the dependencies listed in thepackage.jsonfile.COPY . .This line copies the rest of the application code from the host machine to the/usr/src/appdirectory in the container.EXPOSE 3000This line tells Docker that the container will listen on port 3000. This is the port that the application will be running on.CMD ["node","index.js"]This line specifies the command to run when the container starts. In this case, it's running the commandnode index.jswhich starts the Node.js application.
Build your Docker Image
docker build -t nodeimage .This will build the docker image.
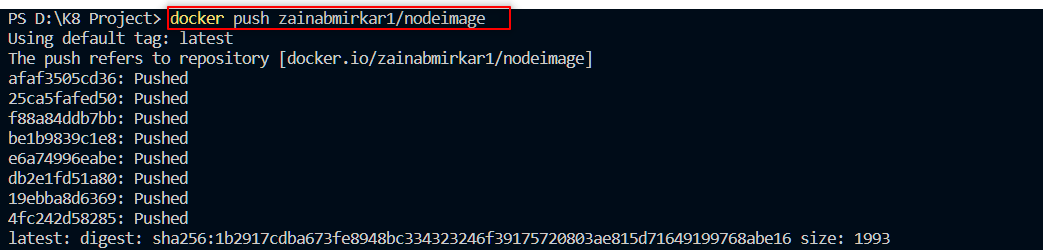
Push your image to Docker Hub
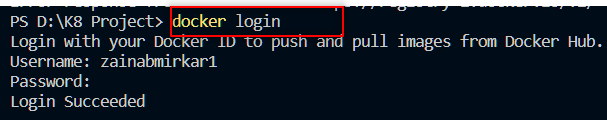
docker loginLogin to Dockerhub by entering your username and password.
Create a remote repository on Dockerhub. I named it examplerepo

Use the
docker tagcommand to tag an image with a new name andpushit to a remote repository. This will tag the image with a new name, and then push it to Docker Hub.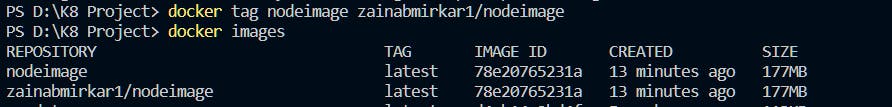
Create deployment.yaml file
A deployment is responsible for creating, updating, and scaling pods, and rolling back to a previous version in case of a failure.
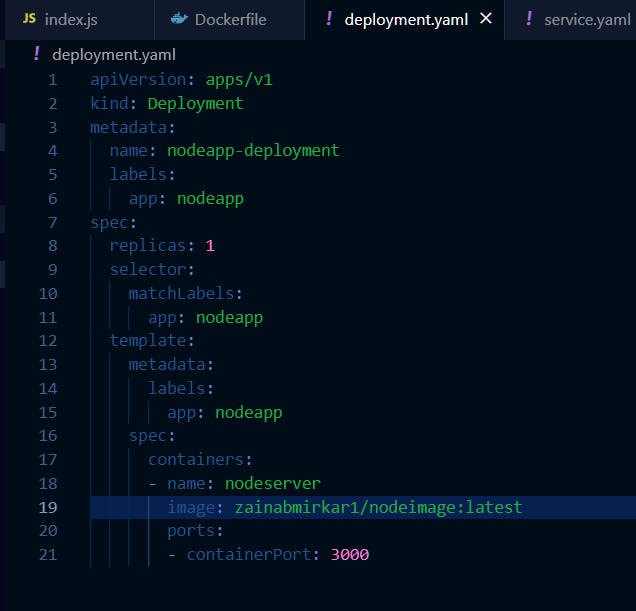
apps/v1, which is the version of the Kubernetes API used to create the deployment.kindspecifies that this is a deployment resource.The
deploymentis named "nodeapp-deployment" and is labeled with "app: nodeapp". A label is a key-value pair that can be added to Kubernetes objects (such as pods, services, and deployments) to organize and identify them.one replicaof the pod should be running at all times.The
selectoris used to determine which pods should be included in the deployment. The pods are selected based on the label "app: nodeapp".The
templatedefines the pod template that the deployment will use to create new pods.The
specfield of the template describes the container that runs inside the pod.The
containeris namednodeserver, it uses thezainabmirkar1/nodeimage:latestimage and containerPort is exposed on3000
Create service.yaml
Services enable communication between pods within a cluster and also provide a stable endpoint for external clients to access the pods.
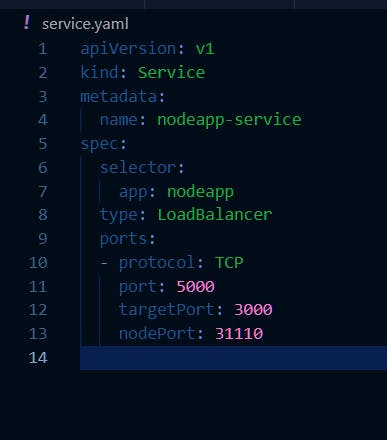
The service type is set to
LoadBalancer, which means that the service will be exposed externally using a load balancer.The service
listenson port5000, which is the port exposed by the load balancer, andforwards trafficto targetPort3000on the pods.The
nodePortfield is set to31110, which means that the service will also be exposed on that port on each node in the cluster.
Deploy your application in Kubernetes
Ensure Minikube is running by
minikube statuskubectl apply -f deployment.yamlKubernetes will read the YAML file and create or update the deployment according to the configuration specified in the file.
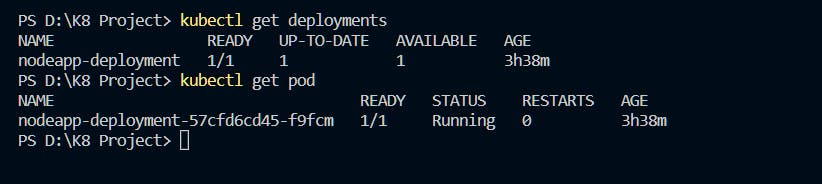
kubectl apply -f service.yamlKubernetes will read the YAML file and create or update the service according to the configuration specified in the file

minikube service nodeapp-serviceThis will give the URL to access the application.
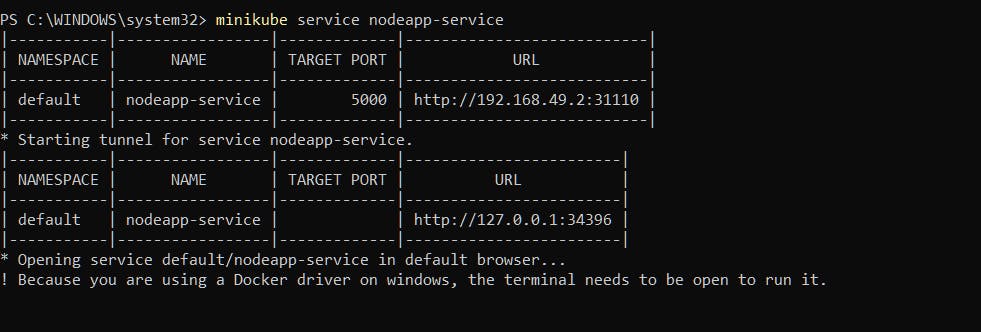
Result